SSC India research
Smart Surfaces Coalition reports
Solving the Heat Threat in India
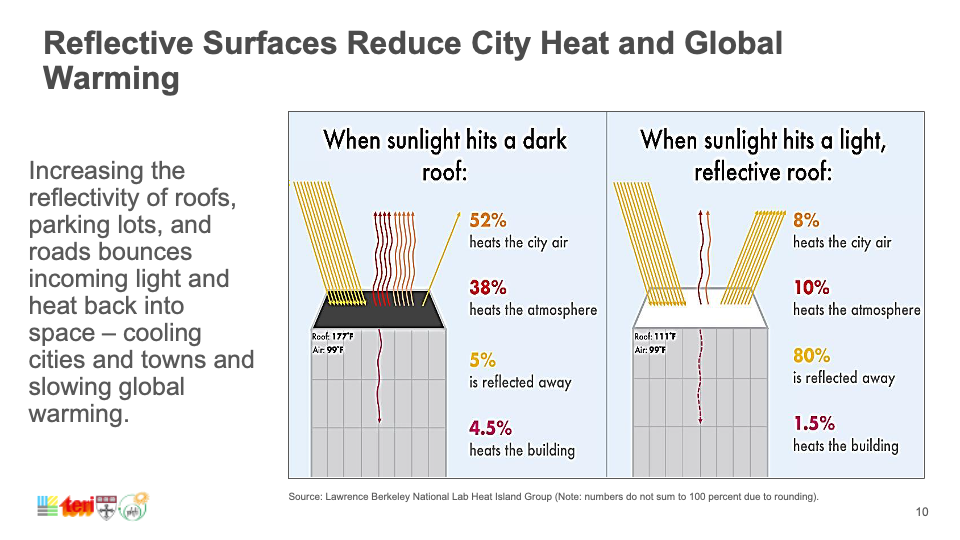
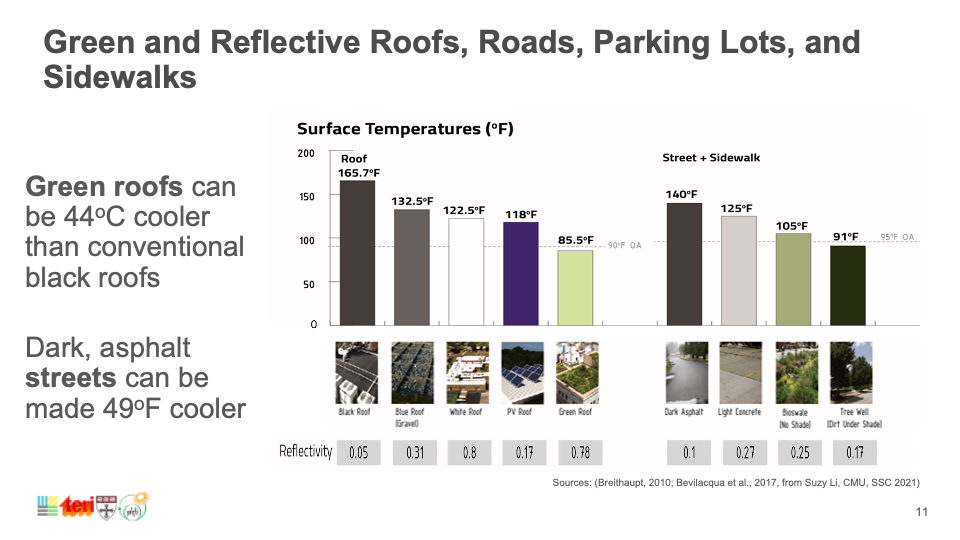
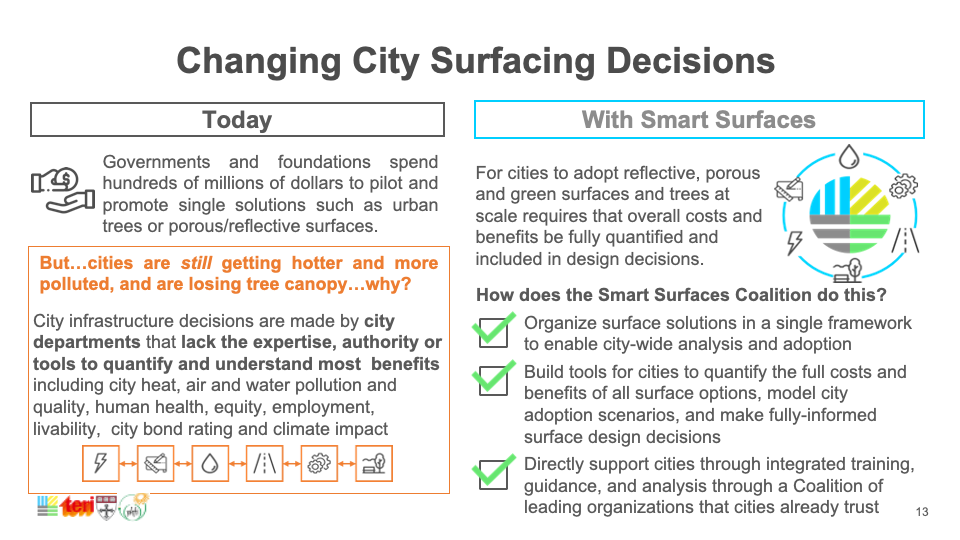
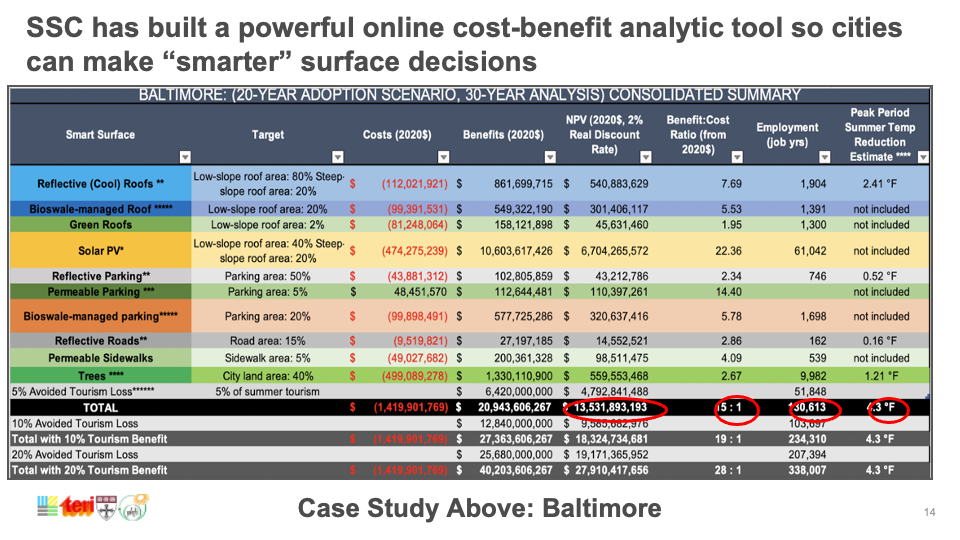
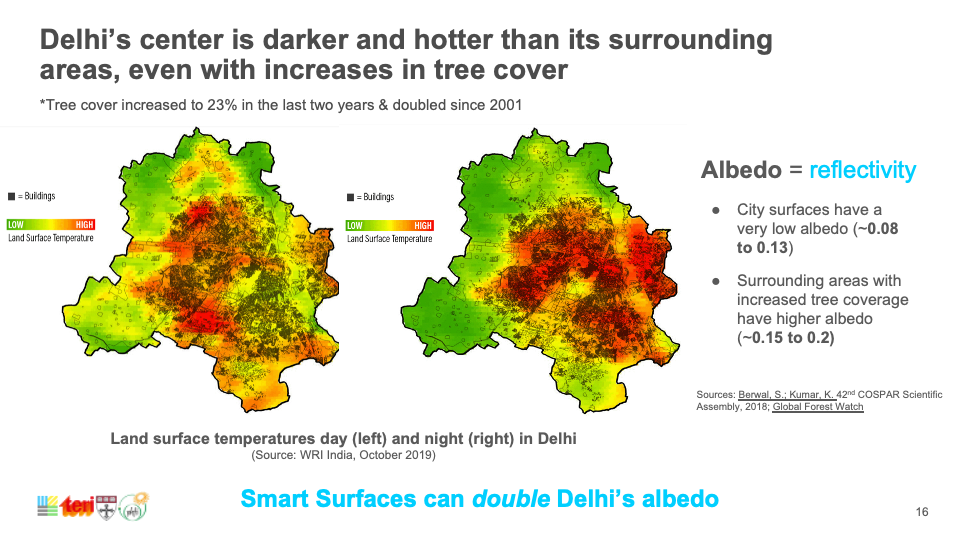
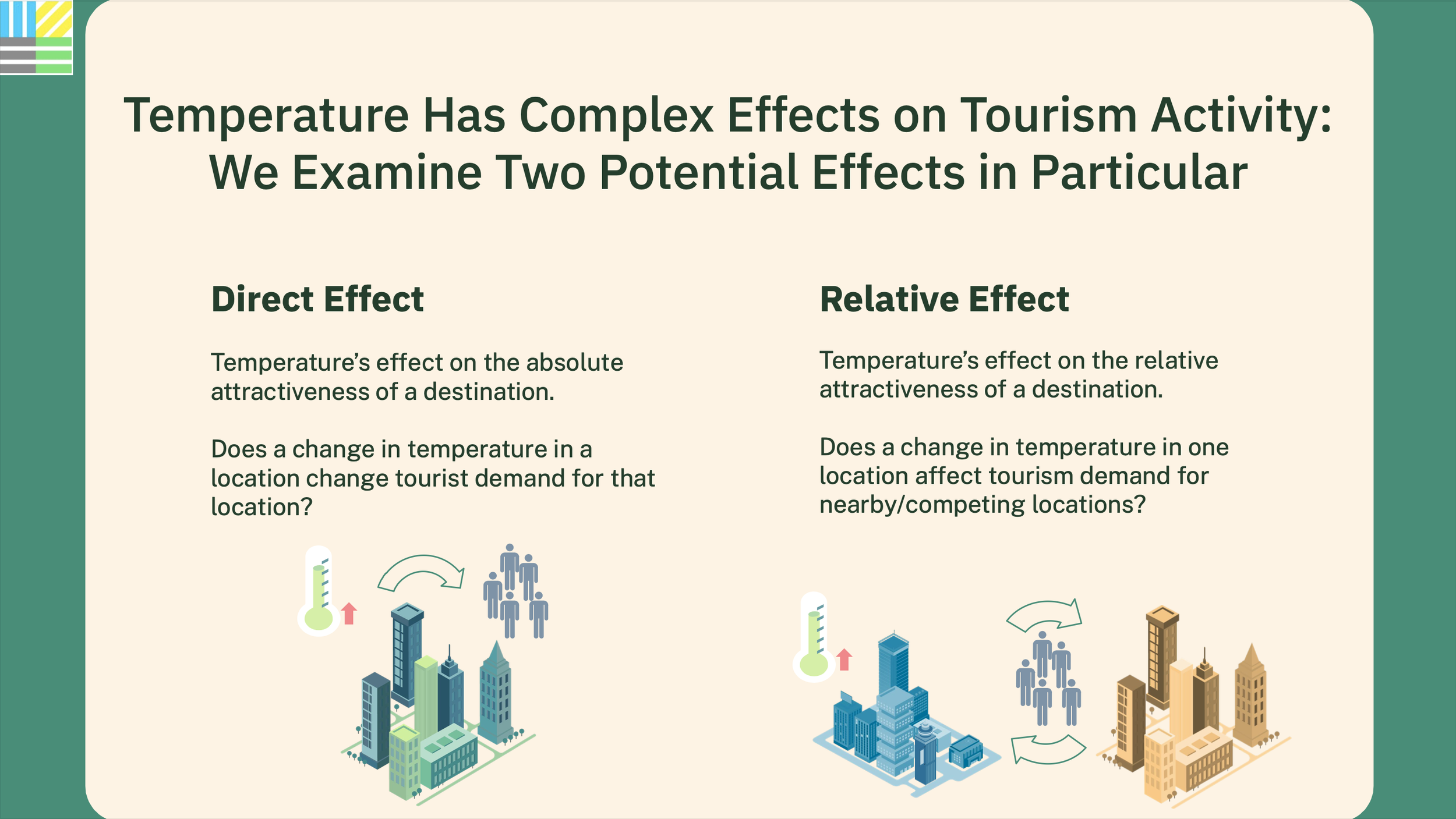
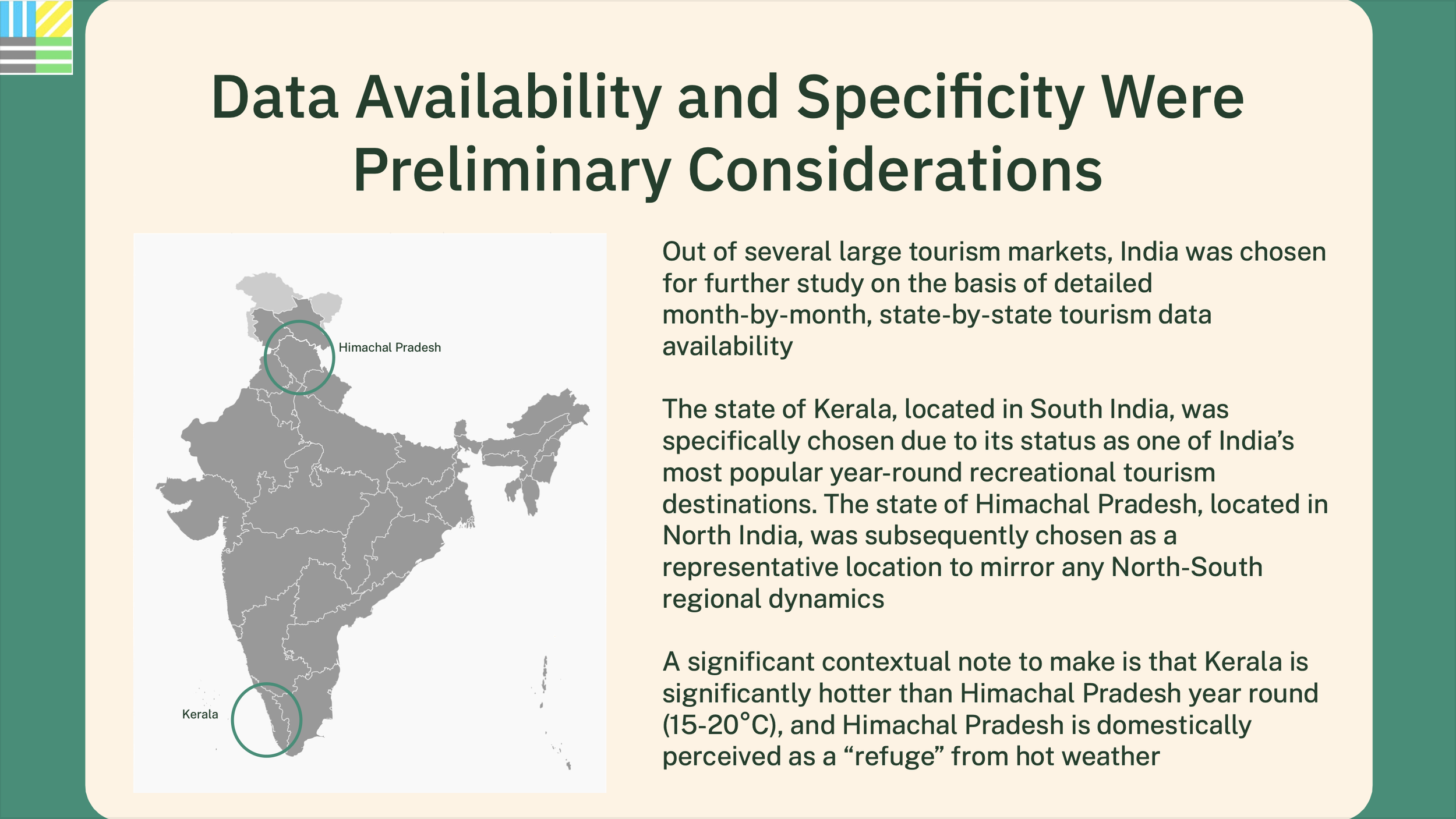
Capping global temperature rise at 1.5˚C necessitates widespread adoption of Smart Surfaces, incorporating reflective, green, and porous elements like trees and solar PV. India, with its large, urbanizing population and high vulnerability to extreme heat, faces risks exacerbated by conventional cooling strategies. Relying on private air conditioners escalates costs, reduces outdoor productivity, and worsens urban heat. Smart Surfaces, doubling city reflectivity, offer a cooling solution through negative radiative forcing, countering global temperature rise. Indian cities like Delhi and Mumbai can lead by adopting these surfaces, cooling by 3˚C, mitigating air conditioning needs, cutting costs, and fostering sustainability.
Healthcare Cost Burden of Heat Islands in Indian Cities
The economic impact of rising temperatures in India is extensive, affecting health, productivity, and healthcare costs. With a projected temperature increase of 4-5°C by the end of the century, heat-related illnesses, including cardiovascular and respiratory issues, are escalating. Direct and indirect costs of heat-related health problems, coupled with air pollution, contribute to a substantial economic burden. The estimated annual healthcare cost due to heat-related deaths is anticipated to reach USD 13.71 billion by 2100, excluding morbidity and productivity losses. This underscores the urgent need for comprehensive interventions to address the multifaceted economic challenges posed by rising temperatures in India.
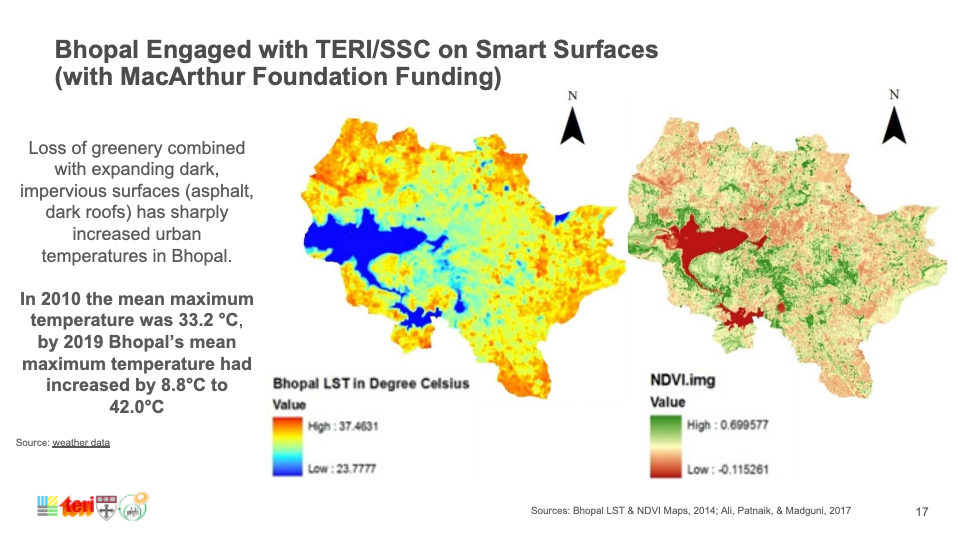
Smart Surfaces for Bhopal
Bhopal, a city of approximately 2.5 million in India, faces a humid subtropical climate with soaring temperatures exceeding 40 °C during peak summer. Heatwaves, once rare in April, are now more frequent. The Green and Blue Master Plan, aligned with smart growth principles, aims to make Bhopal India’s most livable and environmentally sustainable city. Urban forestry initiatives under the plan include creating multi-functional green spaces and targeted tree planting to enhance water quality and reduce urban flooding.
Bhopal is becoming the first South-Asian city to adopt Smart Surfaces with accurate citywide surfaces data (area, albedo, heat) and capacity to quantify and deliver on a citywide integrated cooling strategy.
Smart Surfaces for Indian Schools
India's education sector grapples with the economic burden of excess heat, affecting 250 million students, exacerbated by inadequate infrastructure and high temperatures. Despite government funding, challenges like low student-teacher ratios persist, impacting academic performance and incurring healthcare costs. Unreliable power supply hinders widespread AC, while air pollution, costing $36.8 billion (1.36% of GDP), further degrades learning outcomes, especially for girls. As heat waves become more frequent and intense, innovative solutions like Smart Surfaces for citywide cooling are crucial. Addressing education, climate, and health confluences demands a holistic approach, including infrastructure improvements and resilient cooling strategies for sustainable education in India.
slide decks
articles
India Smart Surfaces Project Health Leads
India Partner Organizations
Useful links to learn more:
National Guidelines for Preparation of Action Plans- Prevention & Management of Heat Waves, National Disaster Management Authority, Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. October, 2019.
Telangana Cool Roof Policy, March 2019.
India Cooling Action Plan, Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change, 2017.
Climate Data Observatory, Climate Centre for Cities, Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
Related TERI project reports:
Patterns of outdoor exposure to heat in three South Asian cities, TERI, July 2019.
Urban Planning Characteristics to Mitigate Climate Change in context of Urban Heat Island Effect, TERI, 2017.